The fascination of mankind with robots is immense. Ever since the first human-like robot was developed in 1868 , there has been a constant development of humanoids and in the recent past , androids. Humanoids are robots designed to resemble the human body , partly or wholly. They are mainly used as a research tool in various scientific areas and are gaining popularity for providing entertainment. Androids are humanoids built to aesthetically resemble humans.
Over the decades , humanoids have improved from being able to perform basic functions such as locomotion to being able to recognize human faces and also display emotions.Such responsiveness of the robots towards external stimuli is a big step in the development of artificial intelligence for robots. A few vital features every modern humanoid aims to have are bipedal locomotion, the capability to interact with humans, a sense of perception of changes in its environment and an ability to learn like the human brain over time. Let’s take a look on these features in detail.
Bipedal locomotion :
This has been quite common in humanoids built over the centuries. Actuators are responsible for motion in robots. The most advanced humanoid, in terms of its proprioceptive capabilities , is the ATLAS built by Boston Dynamics.

ATLAS is capable of lifting and moving around with weights. It can sense its position with respect to its environment with the help of LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) and stereo sensors, enabling it to detect obstacles, assess the terrain and even sense when its being moved.It can move on uneven , even hilly , terrains too. It stands back up when pushed onto the ground (Pretty impressive, ain’t it?) . It uses hydraulic actuators for moving. It has more capabilities than the aforementioned ones and can potentially have an article of its own.
Interacting with humans :
Robots capable of talking to humans have been around for quite some time. Androids such as FACE and HRP-4C can mimic human facial expressions to surprising extents. HRP-4C can sing and dance too ! One of the androids that’ll surely take you by surprise is Erica, the autonomous conversational robot. It responds to speech and responds with its own answer, whilst making human-like facial expressions and jaw movements. Sophia is another android built to communicate, it can turn towards the person talking to it with the help of cameras placed in its eyes and employs facial recognition algorithms.

Detecting external stimuli:
Exteroceptive sensors of various kinds are employed to detect events in the surroundings. CCD Cameras and computer vision are used to perceive visual changes , microphones with speech recognition algorithms. Arrays of Tactels ( tactile sensors ) are used to sense touch. Actroids have been programmed to flinch if they see a slap coming and react normally when tapped on the shoulder.
Autonomous learning:
Machine learning is being improved continually and is currently an active area of research. With machine learning , humanoids can be taught to perform various actions and also learn from previous mistakes and prevent their occurrence in the future. The most notable accomplishment in this field has to be Google DeepMind’s AlphaGo . The program defeated the world’s Go champion Lee Sedol in a five-game series, AlphaGo winning four out of the five games. It uses an artificial neural network and deep reinforcement learning to continually improve itself over time. Such general-purpose AI programs would make a huge impact on the android robot pool.
Conclusion:
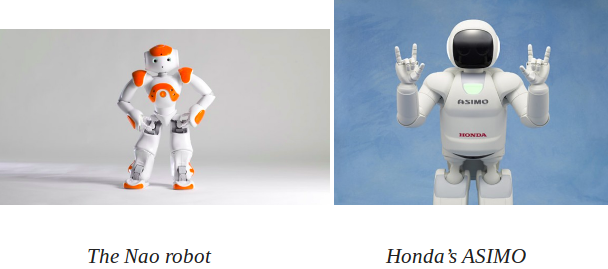
From steam-powered robots to self-learning programs , the robot industry has grown rapidly and continues to do so. The cute Nao robots can play soccer and golf , Honda ASIMO has been featured in a 15-minute show at Disneyland and the android Geminoid F also stars in a movie ! Robots continually pervade into the daily life of human beings and it won’t really be a surprise if we find robotic assistants in our homes in the future .
